Uses of Artificial Intelligence healthcare
Precision in Cancer Diagnosis
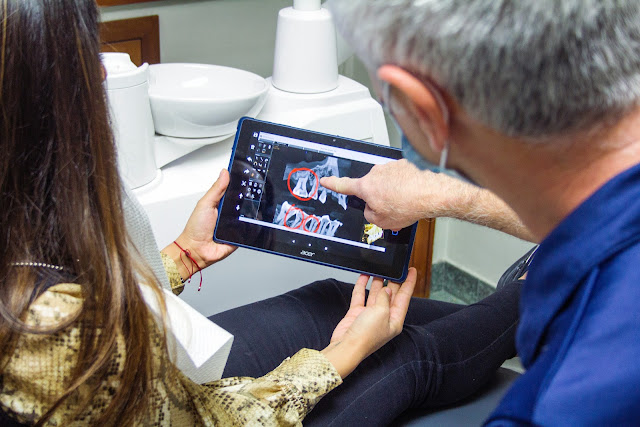
PathAI is an effective technology for machine learning and artificial Intelligence in healthcare. PathAI enables pathologists to make precise diagnoses.
PathAI lowers errors in the cancer diagnostic process. It provides a variety of new methods for customized medical care. Cancer patients get diagnosed more accurately. Artificial Intelligence in medicine helps start treatment before it becomes fatal.
Early Detection of Deadly Blood Diseases
Artificial Intelligence in medicine is a massive asset. It comes in handy in the early diagnosis of potentially fatal blood-related disorders. Thanks to AI-enhanced microscopes, doctors can now examine blood samples for harmful substances and microorganisms. Examples include Staphylococcus, E. coli, etc. The examination is possible to happen faster than they could with manual scanning.
Researchers looked at more than 25,000 images of blood samples to train the machines to find harmful germs. The robots learnt to recognize these germs in the blood. They could forecast their presence in fresh samples.
Thanks to artificial Intelligence healthcare, this attained a 95% accuracy rate. It drastically reduced the fatality rate.
Online medical assistants
Virtual health assistants are in charge of various tasks. The tasks include answering routine patients' calls and emails. It involves keeping their medical information while protecting sensitive data. Also, setting up doctor appointments is part of the responsibility. The assistants remind patients of follow-up visits and clinical meetings.
Applications for Artificial Intelligence healthcare throughout Africa:
Uganda- A group of Makerere University students developed Matibabu App, an app to help test Malaria. The idea was to avoid pricking needles into the patient's body. They created the "Matibabu" device that tests Malaria by scanning the patient's finger.
South Africa- the Phillips Foundation successfully rolled out Delft Imaging's AI software in 11 hospitals in South Africa. With X-ray imaging, COVID-19 patients are triaged and kept under observation. The AI-based CAD4COVID program from Delft Imaging complements COVID-19 diagnostic tools. It uses commonly accessible chest X-rays. It evaluates the severity and course of COVID-19 disease.
Tanzania and Zambia- The CAD4TB program (Delft Imaging) is from the Delft Institute. It is used in Tanzania and Zambia to evaluate the effectiveness of computer-aided analysis of pulmonary tuberculosis from chest radiographs.
Antara Health uses AI-assisted health technology to simplify healthcare for patients and providers.
The possibilities of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
One, Artificial Intelligence in medicine helps create personalized medication. The technology first analyzes a person's gene expression. It then identifies the best appropriate medical regimen. It also seeks out defects and highlights them. It gives one a fighting chance to prevent possible future deficiencies for them and their generation.
Artificial Intelligence in healthcare analyzes sizable volumes of data. It helps spot and provide the best possible route to a long life. It is similar to "google maps" for a healthy, lengthy life.
Second, Artificial Intelligence in healthcare has allowed a shorter response time to most medical conditions. (In Countries where it got embraced). It has given room to save many lives by way of early detection.
Third, it's not just early detection anymore. Artificial Intelligence in medicine makes it possible to get incredible accuracy. It is so, even from similar symptomatic displays. It helps mitigate the possibility of misdiagnosis.
Lastly, we cannot discuss Artificial Intelligence in healthcare and skip the beautiful idea of medical nanites. The possibilities of what good can come from Artificial Intelligence in medicine are refreshing.
The Sustainable Development Goals allow for the possibility of the integration of AI and medicine in SDG 3:
Achieving 13 targets encompassing a wide range of WHO work will help ensure healthy lifestyles and advance everyone's well-being at all ages. Nearly every single one of the 16 aims is related to enhancing one's health.
Goal 3.1 of Maternal Mortality: Already incorporates AI. Between 2000 and 2017, the global MMR (average maternal deaths for every 100,000 live births) reduced by about 38% worldwide.
94% of maternal deaths occur in low- and lower-middle-income countries. Imagine the impact Artificial Intelligence in healthcare will have in Africa!
Sub-Saharan Africa has the highest neonatal mortality rate in the world. It has (27 deaths in every 1000 live births), with 43% of global newborn deaths. It is followed by Central and Southern Asia (23 deaths per 1000 live births), with 36% of global newborn deaths.
What if the medical staff could use Artificial Intelligence in medicine to monitor the baby more intently? The medics could "edit out defective genomes giving the newborns a greater fighting chance.
What are the ethical implications of AI in the medical field?
Although the use of AI in clinical settings holds great promise for enhancing healthcare, it also raises ethical concerns that we must now address. Read further on the ethical implications of AI.